Spark could be used as ETL tools, today we are going to walk you throught how to and explain the required Spark knowledge.
Spark Overview
Spark Core: have to have it
- Fundamental Component
- Task Distribution
- Scheduling
- input/output
Spark SQL : We will use this for our ETL tools
Spark Streaming: we don’t need it
- Streaming analytics
- Micro Batches
- Lambda Architecture
MLlib : we dont’ need it
Spark Install and run
- Download spark from here
-
run following from the download folder
tar -xvf spark-2.4.7-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz -
mv to /usr/share
sudo mv spark-2.4.7-bin-hadoop2.7 /usr/local/ -
Add to path
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/spark-2.4.7-bin-hadoop2.7/bin:/usr/local/spark-2.4.7-bin-hadoop2.7/sbin -
start the master:
start-master.sh - verify http://localhost:8080
Spark Data Concepts
RDD - Resilient Distributed Dataset, container that all you to work with data object.
DataFrame - data table
Dataset - combination of RDD and DataFrame, this is the objects we are going to work with1
How Spark cluster works
Official document is here. I suggest to read throug the detail of how cluster works, that is very clear.
There are 3 type of clusters that spark can run on:
- Standalone
- Mesos
- Yarn
I am only going to discuss the standalone. Here is picture of cluster:
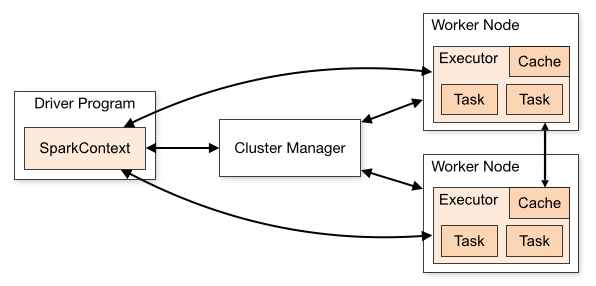
Cluster Manager is the master process in spark, this is where you run ./sbin/start-master.sh. You only have 1 cluster manager in a cluster.
Driver AKA Driver Program in this picture, is responsible for converting a user application to smaller execution units called tasks and then schedules them to run with a cluster manager on executors. The driver is also responsible for executing the Spark application and returning the status/results to the user. Spark Context is created by Driver Manager and act as context between Driver and Cluster Manager, it can be used to create RDDS, accumulators and broadcast variables.
Worker Node could be machine, docker container or virtual machine.
Executor is the processer that will run your task, a node can contain many Executor
To Run your application in above picture, there are 2 steps:
-
submit applicationsthis is same asdeployment, you send your jar file to cluster, and then cluser manager give them toWorker Node. -
Run the task, task will be run on theWorker Node, and result will be sent back toDriver ProgramviaSpark Context.
Spark Development Cycle
spark-submit
for client program to work in spark cluster, you need to use SparkLauncher to connect to spark cluster, then submit your spark application for spark cluster to run. using SparkLauncher has no different as using spark-submit command at spark shell, the command like following:
spark-submit --executor-memory 4g --driver-memory 4g --verbose \
--jars $JARS \
--class "" \
$JAR_FILE \
--config $CONFIG_FILE \
--R $RUNTIME_PARAMETERS \
--jobname $1
so in the SparkLauncher you need to specify corresponding parameters as spark-submit
SparkAppHandle handle = new SparkLauncher()
.setAppResource("/my/app.jar")
.setMainClass("my.spark.app.Main")
.setMaster("local")
.setConf(SparkLauncher.DRIVER_MEMORY, "2g")
.startApplication();
you also can use launch() instead of startApplication(), but that require
you to control the child process.
use the launch(), then you can use spark.waitFor() to handle the exit:
int exitCode = spark.waitFor();
minimum setter for launcher:
setSparkHomesetAppResource- you spark application jarsetMainClasssetMaster
above are the minimum setter required for spark launcher.
-
.addJar- This to add your application dependencies jar, you can also use set conf withDRIVER_EXTRA_CLASSPATHorEXECUTOR_EXTRA_CLASSPATHsame. -
.addFile- submit the file that your spark application need, usually for log file, csv file and config file -
deployMode- useclientas for testing, useclusterfor prodction
here has very good artile to explain
Spark Cluster Configuration
Rules of Thumb:
- RAM Size: Total RAM Size should be 3 times of the total file/data loaded on the Cluster, eg: you want to load 5GB data, then you cluster total RAM size should be 15 GB.
- Disk Size: Loaded data spills into the disk when RAM is full, so Disk size shoudl at least be equal to RAM size, eg: if node RAM size is 5GB, then at least the disk size need to be 5 GB.
- No. of executor per node: 10 executor per node.
- No. of cores per node: Recommended as equal to the no. of executor
the No. of executor/cores are for start plan, you can adjust depends on the node’s hardware setup.
Setup Environment
I use Gradle and java, so this project will NOT have any Scala or Python or Maven, following is the build.gradle, it list all the depencies we need
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'org.apache.spark:spark-core_2.11:2.4.4'
implementation 'org.apache.spark:spark-sql_2.11:2.4.4'
runtimeOnly 'mysql:mysql-connector-java'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
Extractor: Connect to MySQL database
-
Create
SparkSessionSparkSessionis single point of Spark Framework entry to interact withDataFrameandDataSet, with Spark 2.0,SparkSessionbecome simple to create:SparkSession spark = SparkSession.builder() .appName(jobName) .config("some option", "some value" //.enableHiveSupport() .getOrCreate(); //set up sparkSession runtime arguments spark.conf().set("spark.sql.shuffle.partitions", 6); spark.conf().set("spark.executor.memory", "2g");If you are running on Hive FS, then you can
enbableHiveSupportoption, otherwise, it use “in memory”.you can use following code to print out all the runtime arguments
Map<String, String> sparkConf = spark.conf().getAll();the
spark.sql.shuffle.partitionsis the number of partition when spark shuffle the data for join and aggregation. Here is good link to introduce the “shuffle” and “sort” inMapReduced. -
Implement
DataFrameReaderOnce you have the
SparkSession, you can buildDataFrameReaderfrom it:DataFrameReader rdr = spark.read(); rdr.format("jdbc"); rdr.option("numPartitions", 10); rdr.option("partitionColumn", "Country Code"); //JDBC connection properties final Properties connectionProperties = new Properties(); connectionProperties.put("user", MYSQL_USERNAME); connectionProperties.put("password", MYSQL_PWD); String dbTable = "(SELECT * FROM HNPQCountry) AS t"; long start_time = System.currentTimeMillis(); Dataset<Row> jdbcDF = spark.read() .jdbc(MYSQL_CONNECTION_URL, dbTable, connectionProperties);Set
formatforDataFrameReader:rdr.format("jdbc");format: DataFrame Source Data Format: json,csv (since 2.0.0),parquet (see Parquet),orc,text,jdbc, libsvm.jdbc: This will connect to database with jdbc connection, there are 3jdbc()methods:jdbc( url: String, table: String, predicates: Array[String], connectionProperties: Properties): DataFrame jdbc( url: String, table: String, properties: Properties): DataFrame jdbc( url: String, table: String, columnName: String, lowerBound: Long, upperBound: Long, numPartitions: Int, connectionProperties: Properties): DataFrame -
Read through the
DataSet:System.out.println(jdbcDF.schema()); jdbcDF.show();
Start ETL Job: Cluster Mode VS Standalone Mode
-
Cluster Mode
You will use
SparkLauncherto ‘submit’ the ETL job to cluster, basically you need config following parameters and callsubmit(), this is no different as you callsubmitfrom spark shell.as you can see the “main class” is
SimpleSparkEtlJobApplication, this class willassemblythe JobRunner and then callrun()method to start the process. TheAssemblywork contains 2 steps:- Take the pass-in parameter
configFilepass toJobConfigModuleBuilderto genereateJobConfigfile - The
JobConfigModuleClassNamefrom theJobConfigand then build it. e.g. in our example, theJobConfigModuleClassNameisSampleJobRunnerConfigModule.
After
JobConfigModulecreated, then use google guice to inject that class forJobRunnerand then callrun()method of that JobRunner. - Take the pass-in parameter
-
Standalone Mode
Standalone Mode is different as cluster mode since we can pre-intialize the
JobConfig,SparkConfigandJobRunnerinstance, but the concept is same: use IoC (not google guice, we use spring boot) to prepare all the instance JobRunner need and then “inject” into JobRunner.The
SampleJobSparkConfigStandaloneis example to show to config the standalone spark job
«««< HEAD
predicate
I used predicate when I use JDBC SQL, my understanding is: use `Predicate`
you can `chop` the WHERE clause into multiple group, and each `Predicate`
will use 1 spark partition and create 1 JDBC connction. =======
~~~java
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:spark-config-standalone.yml")
@ConfigurationProperties
@Getter
@Setter
public class SampleJobSparkConfigStandalone {
private String jobName;
private String master;
private String partition;
private String dbConnectionURL;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String dbTable;
@Bean(name = "SampleJobConfig")
public JobConfig sampleJobConfig(){
JobConfig sampleJobConfig = new JobConfig();
sampleJobConfig.setDbConnectionURL(this.dbConnectionURL);
sampleJobConfig.setUserName(this.userName);
sampleJobConfig.setPassword(this.password);
sampleJobConfig.setDbTable(this.dbTable);
return sampleJobConfig;
}
@Bean(name = "standaloneSparkConfig")
public SparkConfig standaloneSparkConfig(){
SparkConfig sparkConfig = new SparkConfig();
sparkConfig.setJobName(this.jobName);
sparkConfig.setMaster(this.master);
Map<String, String> sessionConfigs = new HashMap<>();
sessionConfigs.put("spark.sql.shuffle.partitions", partition);
sessionConfigs.put("spark.executor.memory", "2g");
sparkConfig.setSparkSessionOptions(sessionConfigs);
return sparkConfig;
}
@Bean(name = "standaloneJobRunner")
public JobRunner standalonJobRunner(JobConfig sampleJobConfig ){
Extractor<SampleJobEvent> sampleExtractor = new DBDataExtractor();
sampleExtractor.setJobConfig(sampleJobConfig);
Transformer<SampleJobEvent> sampleTransformer = new SampleTranformer<>();
Loader<SampleJobEvent> sampleLoader = new SampleLoader<>();
JobRunner jobRunner = new JobRunner(sampleJobConfig, sampleExtractor, sampleTransformer, sampleLoader);
return jobRunner;
}
}
~~~
Spark Config
Spark Config has all the information for creating SparkSession object, plus it also carry information that SparkLauncher need when run in cluster mode.
Spark Config is used by who want to start the spark job:
- it is
SparkSubmitterif run in cluster mode - it is
SimpleSparkEtlServiceif run in standalone mode
they use SparkConfig to create a SparkSession and then pass the SparkSession to JobRunner.run()
78faef95b2f147e907f1f5aeede129c76742fad0