External Config let you config all the service in 1 place, the benefit is not in the scope of this article.
Resource
Source code repo: https://github.com/R0NGSH3N/spring-cloud-template
Spring official site: https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud-config
There are 2 parts of Spring Cloud Config
1.Config Server - where all the configuration of the service at
2 Config Client - plug into each service that help service to retrieve configuration from server.
Spring Cloud family:
| Component name | Function Description |
|---|---|
| Spring Actuator | Monitor your application’s health |
| Eureka/Zookeeper | Service Registration provider(for Service Discovery) |
| Ribbon | Load Balancer (for service) |
| Feign (Client) | replacement of RestTemplate/Web Client |
| Hystrix | isolate failed service |
| Spring Cloud Gateway | Microservice Gateway |
| Spring Cloud Config | Externalized Config |
| Spring Cloud Slueth | Provide (Services) Distributed Tracing |
Spring Config Server
Since we are going to put all the service’s config files together in some where, so the name will not be application.yml any more, the file name will be application name.yml, eg:
service name: producer-helloworld-service
application config file at config server: producer-helloworld-service.yml
Set up Git Repository as backend for config server
In this approach, The config files will be put in a separate git repo!, it could be put as per repo per application(service) or per repo per profile.
I prefer per repo per profile, that means I will have 4 git repo(per report per profile): dev,qa,uat,prod
The detail information: https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-config/multi/multi__spring_cloud_config_server.html
Set up File System as backend for config server
You also can put config into the local, so you don’t need those git repo. but you need to start config server as native
1.Change your config server application.yml in config server like following:
server:
port: 9001
spring:
profiles:
active: native
cloud:
config:
server:
native:
searchLocations: classpath:config-repo/${profile}
management:
security:
enabled: false
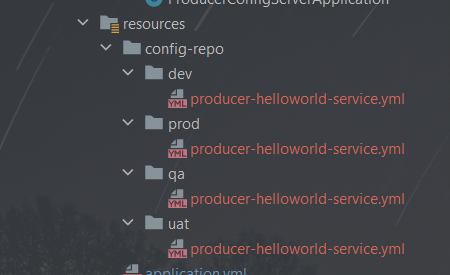
2.copy config-repo to config server project’s resources folder
How server find your yml file?
Once complete the config, start the server, then go to http://localhost:9001/producer-helloworld-service/dev
you can see the structure of restful path is different as the config file in file system. Depends on how you set up the config file structure, the query path will be different, following are some structures that Spring suggest.
here is the config files on my local file system:
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties
application: is your service name, in my example, application = producer-helloworld-service
I define profile as environment: dev, qa,uat,prod
label usually is version, I don’t have label here.
So, obviously, I am using the first structure which I think more most of sense.
I will use yml as config file format.
put all the configs in central location without config server
If you don’t use git to versionize your config file (which I don’t), you don’t really need config server to manage your config, you can use --spring.config.location parameter to specify your config location. Following command is how I start the test service with that parameter:
java -jar producer-helloworld-service-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.config.location=file:///WHATEVER_PATH/config-repo/dev/producer-helloworld-service.yml
Spring Config Client
On client side, if you don’t have following dependency, add them in build.gradle:
implementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-config'
and also need to add dependencyManagement”
dependencyManagement {
imports {
mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:${springCloudVersion}"
}
}
and finally specify the spring cloud replease version:
ext {
set('springCloudVersion', "Hoxton.SR7")
}
the Full build.gradle file looks like following:
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.3.4.RELEASE'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.0.10.RELEASE'
id 'java'
}
group 'org.r0ngsh3n.springcloud.service'
version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
ext {
set('springCloudVersion', "Hoxton.SR7")
}
dependencies {
implementation 'com.h2database:h2'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-validation'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator'
implementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-config'
testImplementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test') {
exclude group: 'org.junit.vintage', module: 'junit-vintage-engine'
}
}
dependencyManagement {
imports {
mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:${springCloudVersion}"
}
}
Since the application.yml is the local config file, we can’t use any more, to force this application to fetch the config from server, we need to create a file called bootstrap.yml, when spring find this file, it will read the config from bootstrap.yml over the local application.yml.
As you can think of, the bootstrap.yml need 3 type of information to retrieve config from server:
1.Application name: since there are tons of application config on the config server, you need to “identify” yourself to the server.
2.Profile: as we stated earlier, I prefer to use profile as environment: dev/qa/uat/prod. So specify different profile in bootstrap.yml will end up retrieving different environment/profile config.
3.Server URI, too simple, you need to know where is config server running at.
So the bootstrap.yml file looks like following:
spring:
application:
name: producer-helloworld-service
profiles:
active: dev
cloud:
config:
uri: http://localhost:9001